Acts of unlawful interference (AUI), attempted thefts carried out with safety violations can give rise to emergency situations with the loss of human life, large financial damage and halt production.
Operational disorder or work interruptions could result in the loss of economic management at the municipal or regional levels as well as in a significant decrease of the population life safety.
Regulations on the use of safety equipment at the sites of FEC (Fuel and Energy Complex) are defined in subordinate acts of the Federal Law N 256-FZ of 21 July 2011 “On safety at the sites of Fuel and Energy Complex”.
Entrance to the sites is by identification card. Visitors’ access except on the grounds is prohibited.
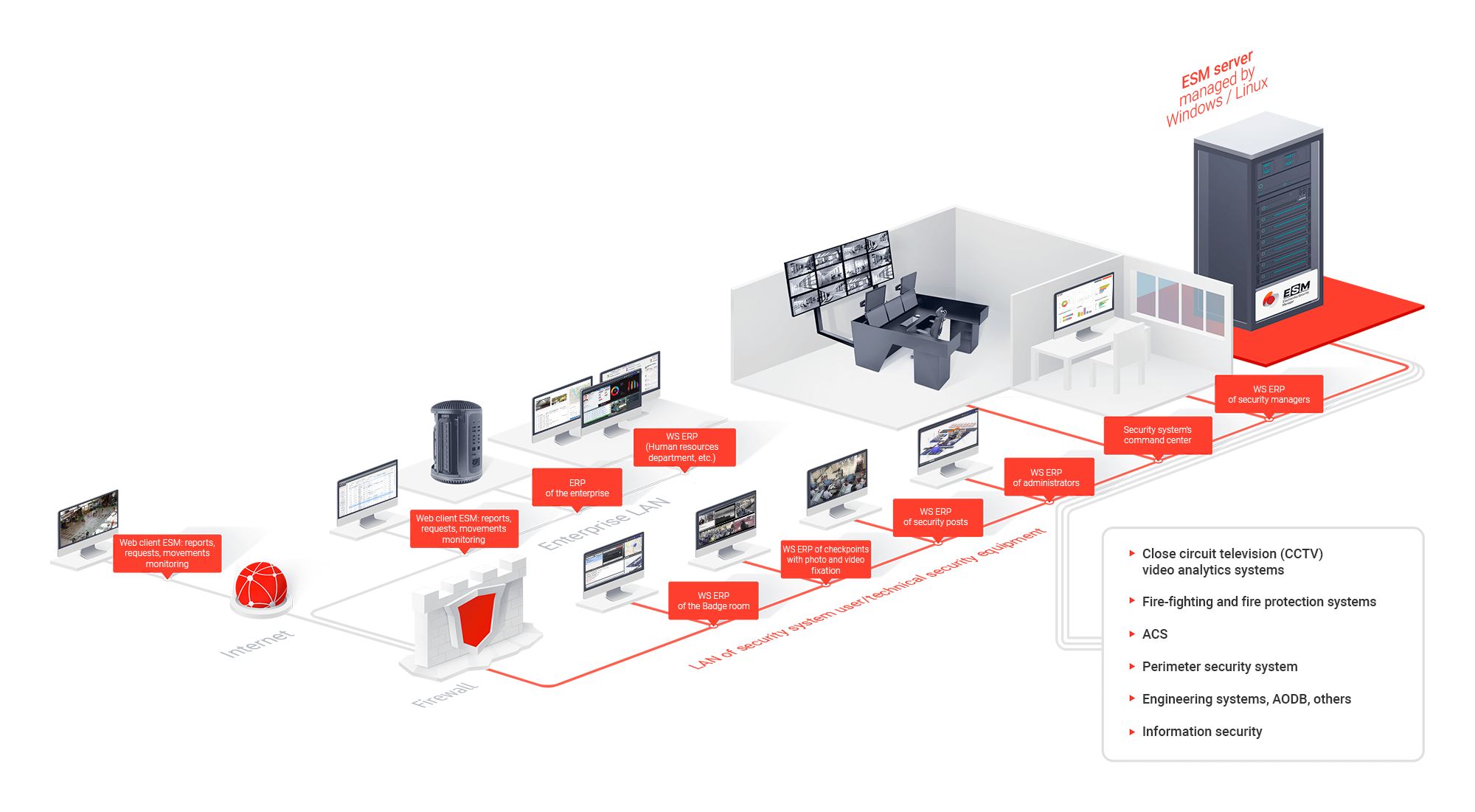
The following secure subsystems are integrated into the hardware-software solution by the principle of “one-stop shop”: access control systems, videosurveillance systems, systems for protecting the perimeter, intruder detection and alarm systems, secure lighting and others.
- Systematic theft of liquid raw materials, end products, equipment, fuel.
- Accidents related to violations of the technological process, safety or contrived by a dissatisfied employee.
- Accidents related to equipment failure due to aging (e.g. fuel leaks from pipelines due to corrosion).
- Accidents related to the situation of strain due to structural deformation (e.g. heavy accumulation of motor transport on bridges, snow accumulation on roofs, etc.).
- Terrorism.
- Opening of storages (containers, boxes, etc).
- Violation of work discipline (which may lead to non-performance of job functions).
- Unauthorized presence of vehicles and people in access-controlled areas.
- Violation of the vehicle movement plan on the territory of the enterprise (unloading/loading).
- Disorder of wells for the extraction of raw materials.
- Inefficient use of resources (electricity, water, gas, etc.).
- Risk reduction associated with potential threats (industrial accidents, environmental pollution with a threat to the life and health of staff, economic losses, and the threat of a terrorist attack).
- Security command center.
- Perimeter.
- Infrastructure lines and pipelines.
- Hazardous production sites.
- Warehouses and production facilities of hazardous industries.
- Control of entrance and exit of railway transport.
- Parking lots.
- Automation of pedestrian and motor transport checkpoints.
- Efficiency increase of detecting break-in attempts at the facility, and also violations access mode and emergency situations due to integration.
- Improving the efficiency of information security systems, through their integration into united integrated security system.
- Automation of decision support by operators in response to security incidents.
- Automation of alarming events’ verification, by the results of which the scenario of its processing is selected.
- Operators’ work control, identifying deviations from incidents’ reaction rules
- Security levels’ management organization.
- Reduction of the enterprise’s losses and the control of the construction works’ progress (control of crossing the enterprises’ territory by railway transport, the identification numbers of railway wagons and tanks, checking with train’s wagon lists, railway tank innage level control, etc.).
- A safety management system that ensures data integration, efficient event processing and alarm signals’ timely transmission to security personnel and management;
- Individual security systems’ level:
-
Access control systems
-
Perimeter protection systems
-
Videosurveillance and video analysis systems
-
Heat monitoring systems
-
Radar and optical systems
-
Facility-based and radio contact alert systems;
-
Global positioning systems (based on GPS / GLONASS) and position finding of moving objects;
-
Specialized applications for managers, where the information filtered by various criteria is transmitted (for example, signals about critical deviations in the work of a particular site, claiming direct intervention of the manager).
-